Best Diabetes-Friendly Diets to Help You Lose Weight
Eating well and maintaining a moderate weight can be important for your health. But if you have diabetes, excess weight may make it harder to manage your blood sugar levels and may increase your risk of some complications. Losing weight can be extra challenging for people with diabetes.
Diabetic diet plan to lose weight
Eating healthfully while you try to reduce weight is important for everyone, but incase of diabetes, choosing the wrong diet could harm your health. Weight loss pills and starvation diets should be avoided, but many popular diets can be beneficial.
There is no one ideal eating pattern for diabetes. Instead, many diets may work well for individuals with diabetes who are trying to lose weight.
Popular diets like the Mediterranean diet, low carb diets, and vegetarian diets can all be good choices.
When considering an eating pattern for diabetes, keep in mind that an ideal diet for diabetes:
- is rich in nutrients
- is high in fiber
- is low in calories
- emphasizes fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats
When you have diabetes, managing your blood sugar is very important. Diets that include regular meals and snacks throughout the day may be better suited to losing weight with diabetes than those that involve long periods without food.
What should you Eat?
If you have diabetes, focus on eating:
- lean protein
- high fiber, less processed carbs
- fruits and vegetables
- low fat dairy
- healthy vegetable-based fats, such as avocado, nuts, canola oil, or olive oil
You also want to manage your carbohydrate intake. Have your doctor or dietitian provide you with a target carb number for meals and snacks. People with diabetes should aim to get about half of their calories from carbohydrates. These would ideally come from complex carbs, fruits, and vegetables.
Experts offers a comprehensive list of the best foods for those with diabetes. Their recommendations include:
| Protein | Fruits and vegetables | Dairy | Grains | Healthy fats |
| beans, such as black, kidney, and pinto | fresh fruit, like apples, avocados, berries, citrus fruits, kiwis, melons, and plums | reduced fat cheese or small amounts of regular cheese | whole grains, such as brown rice, wild rice, whole oats, barley, farro, and quinoa | monounsaturated fats found in avocados, olive oil, nuts, and canola oil |
| nuts and nut spreads, like almond butter, cashew butter, and peanut butter | nonstarchy vegetables, such as asparagus, broccoli, carrots, collard greens, eggplants, kale, mushrooms, okra, salad greens, and tomatoes | low fat, low added sugar yogurt | whole grain foods, like whole wheat pasta and whole grain breads — the first ingredient on the label should have the word “whole” in it | omega-3 fats found in oily fish, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds |
| oily fish, such as salmon, mackerel, tuna, and sardines | canned fruit without added sugars — look for words like “packed in its own juices,” “unsweetened,” or “no added sugar” | |||
| whole eggs | dried fruits, like cherries, figs, prunes, and raisins | |||
| poultry, including chicken, turkey, and cornish hen | ||||
| hummus and falafel | ||||
| lentils, such as brown, green, and yellow | ||||
| tofu or tempeh |
Foods to Reduce
For people with diabetes, certain foods should be limited or consumed in moderation. These foods can cause spikes in blood sugar or contain unhealthy fats.
Foods to avoid or limit can include:
- processed grains, such as white rice or white pasta
- fruits with added sweeteners, including apple sauce, jam, and some canned fruits
- full-fat dairy
- fried foods or foods high in trans fats or saturated fats
- foods made with refined flour, such as white bread
- sugar-sweetened beverages, including soda, some juices, and flavored coffee drinks
- foods high in added sugar, like some flavored yogurts, pastries, cakes, candies, and sweetened breakfast cereals
Everyone’s glucose responds differently to different foods. People living with diabetes as a lifelong chronic illness may still want to enjoy a small treat. You may be able to do this occasionally and make other adjustments to your eating plan to accommodate it.
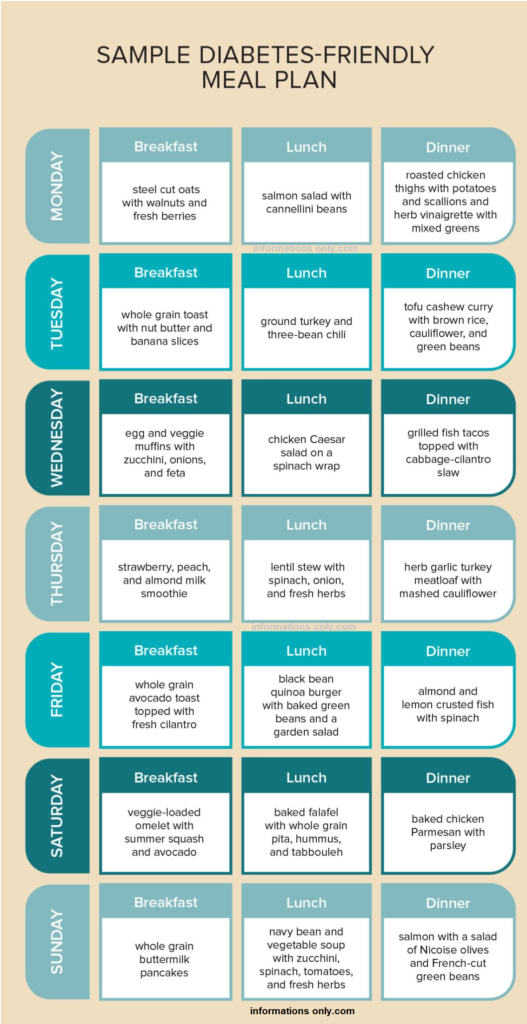
Diabetes-Friendly Diets (Weekly Plan)